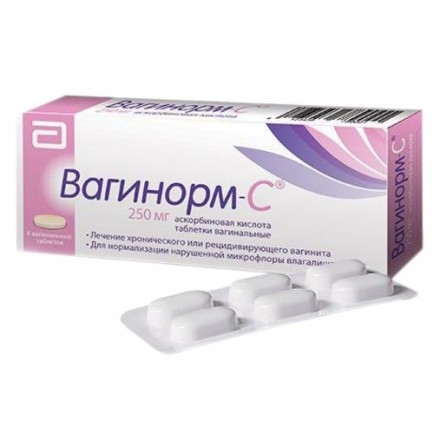
Vaginorm with pills vaginal 250mg N6
Condition: New product
1000 Items
Rating:
Be the first to write a review!

More info
Active ingredients
Vitamin C
Release form
Pills
Composition
1 tablet contains: Active substance: ascorbic acid 250 mg. Auxiliary substances: polymethylsiloxane - 10 mg, lactose monohydrate - 670 mg, hypromellose - 60 mg, magnesium stearate - 10 mg.
Pharmacological effect
Vitamin C. Ascorbic acid is necessary for the formation of intracellular collagen, it is required to strengthen the structure of teeth, bones and capillary walls. It participates in redox reactions, the metabolism of tyrosine, the conversion of folic acid to folinic, the metabolism of carbohydrates, the synthesis of lipids and proteins, the metabolism of iron, the processes of cellular respiration. Reduces the need for vitamins B1, B2, A, E, folic acid, pantothenic acid, helps to increase the body's resistance to infections; improves iron absorption by depositing it in reduced form. It has antioxidant properties. With intravaginal use, ascorbic acid lowers the pH of the vagina, inhibiting the growth of bacteria and helps restore and maintain normal pH and flora of the vagina (Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus gasseri).
Pharmacokinetics
After ingestion, ascorbic acid is completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is widely distributed in body tissues. The concentration of ascorbic acid in blood plasma is normally around 10-20 μg / ml. The concentration of ascorbic acid in leukocytes and platelets is higher than in erythrocytes and in plasma. In deficient states, the concentration in leukocytes decreases later and more slowly and is considered as the best criterion for assessing deficiency than plasma concentration. Plasma protein binding is about 25%. Ascorbic acid is reversibly oxidized to form dehydroascorbic acid, some is metabolized to form ascorbate-2- sulfate, which is inactive, and oxalic acid, which is excreted in the urine. Ascorbic acid, taken in excessive amounts, is rapidly excreted unchanged in the urine, usually It occurs when exceeding a daily dose of 200 mg.
Indications
For systemic use: prevention and treatment of vitamin C hypo-and avitaminosis; providing an increased need for the body in vitamin C during growth,during pregnancy, lactation, with heavy loads, fatigue, during the recovery period after prolonged serious illness; in winter, with an increased risk of developing infectious diseases. For intravaginal use: chronic or recurrent vaginitis (bacterial vaginosis, nonspecific vaginitis), due to anaerobic flora (due to altered vaginal pH); in order to normalize the impaired microflora of the vagina.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to ascorbic acid.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
The minimum daily need for ascorbic acid in the II and III trimesters of pregnancy is about 60 mg. Ascorbic acid penetrates the placental barrier. It should be borne in mind that the fetus can adapt to high doses of ascorbic acid that a pregnant woman is taking, and then ascorbic disease may develop as a withdrawal reaction in a newborn. Therefore, during pregnancy, you should not take ascorbic acid in high doses, except in cases where the expected benefit outweighs the potential risk. The minimum daily need for lactation (breastfeeding) is 80 mg. Ascorbic acid is excreted in breast milk. A mother's diet that contains an adequate amount of ascorbic acid is sufficient to prevent a deficiency in an infant. It is not known whether it is dangerous for the child to use ascorbic acid in high doses by the mother. Theoretically this is possible. Therefore, it is recommended not to exceed the maximum daily intake of ascorbic acid by a nursing mother unless the expected benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Dosage and administration
Applied orally, intramuscularly, intravenously, intravaginally. For the prevention of deficient conditions - 25-75 mg / day, for the treatment of 250 mg / day and more in divided doses. For intravaginal use, ascorbic acid preparations are used in appropriate dosage forms.
Side effects
On the part of the central nervous system: headache, fatigue, insomnia. On the part of the digestive system: stomach cramps, nausea and vomiting. Allergic reactions: isolated cases of skin reactions and manifestations of the respiratory system. On the side of the urinary system: hyperoxaluria and the formation of kidney stones from calcium oxalate. Local reactions: with intravaginal use - burning or itching in the vagina,increased mucous secretions, hyperemia, swelling of the vulva. Others: sensation of heat.
Interaction with other drugs
With simultaneous use with barbiturates, primidone increases the excretion of ascorbic acid in the urine. With the simultaneous use of oral contraceptives, the concentration of ascorbic acid in the blood plasma decreases. its absorption. Ascorbic acid in high doses can reduce the pH of urine, which at the same time reduces analtsevuyu reabsorption amphetamine and tricyclic antidepressantov.Pri simultaneous application of acetylsalicylic acid reduces the absorption of ascorbic acid is about tret.Pri simultaneous use of warfarin effects may decrease varfarina.Pri simultaneous use of ascorbic acid increases iron excretion in patients receiving deferoxamine. When using ascorbic acid in a dose of 500 mg / day, left ventricular function may be impaired. If used simultaneously with tetracycline, urine excretion of ascorbic acid increases. A case of reducing the plasma flufenazine concentration in a patient who received 500 mg ascorbic acid 2 times / day is described. It is possible to increase the concentration of ethinyl estradiol in the blood plasma with its simultaneous use as part of contraceptives for oral administration.
special instructions
Use with caution in patients with hyperoxaluria, impaired renal function, indications of a history of urolithiasis. Since ascorbic acid increases iron absorption, its use in high doses can be dangerous in patients with hemochromatosis, thalassemia, polycythemia, leukemia and sideroblastic anemia. with a high content of iron in the body, ascorbic acid should be used in minimal doses. Use with caution in patients with deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Use ascor ynoic acid in high doses may cause aggravation of sickle cell anemii.Dannye of ascorbic acid diabetogenic action is contradictory.However, with prolonged use of ascorbic acid, blood glucose levels should be periodically monitored. It is believed that the use of ascorbic acid in patients with rapidly proliferating and widely disseminated tumors may aggravate the process. Therefore, ascorbic acid should be used with caution in patients with progressive oncological disease. Ascorbic acid absorption decreases with simultaneous consumption of fresh fruit or vegetable juice, alkaline drink.