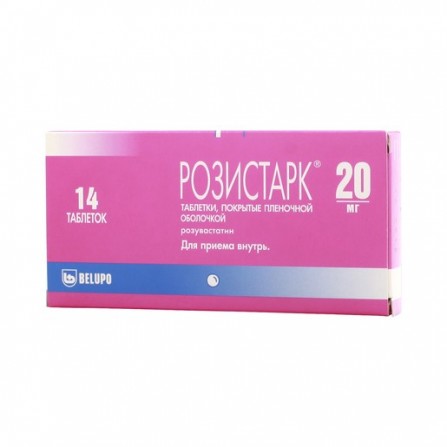
Rozistark pills 20 mg 14 pcs
Condition: New product
1000 Items
Rating:
Be the first to write a review!

More info
Active ingredients
Rosuvastatin
Release form
Pills
Composition
Rosuvastatin calcium 20.8 mg; which corresponds to the content of rosuvastatin 20 mg; excipients: lactose monohydrate - 179.28 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - 85.37 mg, crospovidone - 12 mg, magnesium stearate - 2.55 mg; shell composition: lactose monohydrate - 3.6 mg, hypromellose - 2.52 mg, titanium dioxide - 2.1555 mg, triacetin - 0.72 mg, quinoline yellow - 0.0045 mg.
Pharmacological effect
Lipid-lowering drug from the group of statins. Selective competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase - an enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A to mevalonic acid, which is a precursor of cholesterol. The main target of rosuvastatin is the liver, where cholesterol (Xc) is synthesized and LDL catabolism.; ; Rosuvastatin reduces elevated levels of Xc-LDL, total cholesterol, and triglycerides (TG), increases the concentration of Xc-LPVP, and also reduces the concentration of apolipoprotein B (ApoB), Xc-non-LPVP, Xc-VLDL, TG-VLP and increases the concentration of apolipoprotein AI (ApoA-I) reduces the ratio of Xc-LDL / Xc-HDL, total Xc / Xc-HDL and Xc-non-LPVP / Xc-HDL and the ratio ApoB / ApoA-I; Therapeutic effect develops within 1 weeks after the start of drug therapy, after 2 weeks of treatment reaches 90% of the maximum possible effect. The maximum therapeutic effect is usually achieved after 4 weeks of treatment and is maintained with further regular use of the drug. Clinical efficacy; Rosuvastatin is effective in adult patients with hypercholesterolemia with or without symptoms of hypertriglyceridemia, regardless of their race, gender or age, as well as in the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus and the hereditary form of familial hypercholesterolemia. The drug is effective in patients with hypercholesterolemia IIa and IIb type according to Fredrickson (media The initial concentration of Xc-LDL is about 4.8 mmol / l. In 80% of these patients who received rozuvastatin at a dose of 10 mg, the concentration reaches the target values of Xc-LDL levels established by the European Community for the study of atherosclerosis - less than 3 mmol / l.Patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia who took rosuvastatin in doses of 20 to 80 mg show a positive change in lipid profile.; As a result of titration of doses up to a daily dose of 40 mg (12 weeks of therapy), a decrease in LDL-LDL concentration is observed by 53%. In 33% of patients, the concentration of Xc-LDL is less than 3 mmol / l, corresponding to the target standards of the European Atherosclerosis Research Guidelines. In patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia who took rosuvastatin in doses of 20 and 40 mg, the average decrease in the concentration of Xc-LDL is 22 % In patients with hypertriglyceridemia with an initial TG concentration of 273 to 817 mg / dL, who took rosuvastatin at a dose of 5 mg to 40 mg 1 time / day for 6 weeks, the concentration of TG in the blood plasma significantly decreased; an additive effect was observed in combination with fenofibrate in relation to the content of TG and with nicotinic acid (more than 1 g / day) in relation to the content of HD-C HDL. In patients with low risk of developing coronary heart disease (10-year risk on the Framingham scale less than 10%), with an average concentration of Xc-LDL 4 mmol / l (154.5 mg / dL) and subclinical atherosclerosis, which was estimated by the thickness of the intima-media complex of the carotid arteries (TCIM), rosuvastatin at a dose of 40 mg / day significantly slowed the rate of progression of the maximum TCIM for 12 carotid artery segments compared with placebo with a difference of 0.0145 mm / year (95% confidence interval (CI): from -0.0196 to -0.0093; p less than 0.001). The study was conducted in patients with a low risk of coronary artery disease, for which a dose of 40 mg is not recommended. The dose of 40 mg should be prescribed only to patients with severe hypercholesterolemia and a high risk of cardiovascular diseases. The results of a study on the use of statins for primary prevention showed that rosuvastatin significantly reduced the risk of developing cardiovascular complications with a relative risk reduction of 44%. The effectiveness of therapy was noted after 6 months of use of the drug. There was a statistically significant reduction of 48% of the combined criterion, including death from cardiovascular diseases, stroke and myocardial infarction, a 54% reduction in the occurrence of fatal or nonfatal myocardial infarction and 48% in fatal or nonfatal stroke.Total mortality decreased by 20% in the rosuvastatin group. The safety profile of patients taking rosuvastatin at a dose of 20 mg was similar to the safety profile in the placebo group.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and distribution; Cmax of rosuvastatin in the blood plasma is achieved 5 hours after ingestion. Absolute bioavailability is approximately 20%. Vd of rosuvastatin is approximately 134 liters. About 90% of rosuvastatin binds to plasma proteins, mainly albumin.; Rosuvastatin is mainly absorbed by the liver, which is the main site for the synthesis of Xc and Xc-LDL metabolism.; Systemic exposure of rosuvastatin increases proportionally to the dose. There are no changes in the pharmacokinetic parameters when taking the drug several times a day.; Metabolism; Subject to limited metabolism (approximately 10%). Rosuvastatin is a non-core substrate for metabolism by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. CYP2C9 is the main isoenzyme involved in rosuvastatin metabolism, while CYP2C19, CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 isoenzymes are less involved in metabolism. The main identified metabolites of rosuvastatin are N-desmethyl-rosuvastatin, which is 50% less active than rosuvastatin, and lactone metabolites, which are pharmacologically inactive. More than 90% of the pharmacological activity of inhibiting circulating HMG-CoA reductase is provided by rosuvastatin, the rest is its metabolites. Excretion; About 90% of the dose of rosuvastatin is excreted unchanged through the intestine (including absorbed and unabsorbed rosuvastatin), the rest is excreted by the kidneys. T1 / 2 is about 19 hours. T1 / 2 does not change with increasing dose of the drug. The geometric mean plasma clearance is approximately 50 l / h (coefficient of variation 21.7%). As with other inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase, membrane cholesterol transporter is involved in the process of hepatic uptake of rosuvatatin, which plays an important role in hepatic elimination of rosuvastatin; Pharmacokinetics in particular clinical cases; In patients with mild to moderate renal insufficiency, plasma concentration of rosuvastatin or N-dismethyl-rosuvastatin does not change significantly.In patients with severe renal failure (CC less than 30 ml / min), plasma concentration of rosuvastatin is 3 times higher, and N-dismethyl-rosuvastatin concentration is 9 times higher than in healthy volunteers. The concentration of rosuvastatin in blood plasma in patients on hemodialysis was about 50% higher than in healthy volunteers. In patients with various stages of liver failure (7 points or less on the Child-Pugh scale), an increase in T1 / 2 of rosuvastatin was not detected . However, in 2 patients (8 and 9 points on the Child-Pugh scale) an increase in T1 / 2 was about 2 times. Experience with rosuvastatin in patients with a score of more than 9 points on the Child-Pugh scale is absent. Gender and age do not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of rosuvastatin. Comparative pharmacokinetic studies showed an approximately twofold increase in the mean AUC and Tmax values in patients of the Mongoloid race Japanese, Chinese, Filipinos, Vietnamese and Koreans) compared with the figures of the Caucasians. Hindus showed an increase in the average value of AUC and Tmax by about 1.3 times. Pharmacokinetic analysis revealed no clinically significant differences in pharmacokinetics among the Caucasians and Negroids.
Indications
- primary hypercholesterolemia (type IIa according to Fredrickson, including familial heterozygous hypercholesterolemia) or mixed hypercholesterolemia (type IIb according to Fredrickson) as a supplement to the diet, when diet and other non-drug therapies (for example, physical exercises, weight loss) are insufficient; - a homozygous form of hereditary hypercholesterolemia as an adjunct to diet and other lipid-lowering therapy (for example, LDL-apheresis) or in cases when such therapy is not sufficiently effective ;; - ipertriglyceridemia (type IV according to Fredrikson) as a supplement to the diet ;; - to slow the progression of atherosclerosis as a supplement to the diet in patients who have been shown therapy to reduce the concentration of total Xc and Xc-LDL ;; - reduce the risk of major cardiovascular complications ( cardiovascular death, stroke, heart attack, unstable stenocardia and arterial revascularization) in adult patients with the presence of increased risk factors for cardiovascular atherosclerosis (such as, increased concentration of i C-reactive protein, age, arterial hypertension, low concentration of Hc-HDL,smoking and a family history of early onset of coronary heart disease) ;; - primary prevention of major cardiovascular complications (stroke, heart attack, arterial revascularization) in adult patients without clinical signs of coronary heart disease, but with an increased risk of its development (age over 50 years for men and over 60 years for women, increased concentration of C-reactive protein (more than 2 mg / l) in the presence of at least one of the additional risk factors such as hypertension, low concentrations of HD-HDL, smoking, family history of early development CHD).
Contraindications
For pills 10 and 20 mg; - liver disease in the active phase, including a persistent increase in liver transaminase activity and any increase in serum transaminase activity by more than 3 times compared to VGN ;; - severe renal failure (CC less than 30 ml / min ) ;; - myopathy ;; - simultaneous use of cyclosporine ;; - patients predisposed to the development of myotoxic complications ;; - women of reproductive age not using reliable contraceptives ;; - pregnancy ;; - lactation (breastfeeding) period ;; - age under 18 years of age (efficacy and safety have not been established) ;; - lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption (because the drug contains lactose) ;; - hypersensitivity to rosuvastatin or any of the components of the drug; liver in the active phase, including a persistent increase in liver transaminase activity and any increase in serum transaminase activity by more than 3 times compared to VGN ;; - moderately severe renal failure (CC less than 60 ml / min) ;; - myopathy ;; - simultaneous administration of cyclosporine ;; - myotoxicity while taking other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors or a history of fibrates ;; - hypothyroidism ;; - personal or family history of muscular diseases ;; - excessive use of alcohol ;; - conditions which can lead to an increase in the concentration of rosuvastatin in the blood plasma ;; - simultaneous administration of fibrates ;; - women of childbearing age who do not use reliable contraceptive methods ;; - pregnancy ;; - lactation (breastfeeding) ;; - age up to 18 years (efficacy and safe ness not established) ;; - patients of the Mongoloid race ;; - lactose intolerance,lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption (because the drug contains lactose) ;; - hypersensitivity to rosuvastatin or any of the components of the drug. With caution: For pills 10 and 20 mg; There is a risk of myopathy / rhabdomyolysis - renal failure, hypothyroidism; an indication in a personal or family history of hereditary muscular diseases, an indication of a history of muscle toxicity in the use of other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors or fibrates; excessive drinking; conditions in which there is an increase in the plasma concentration of rosuvastatin; age over 70 years; history of liver disease; sepsis; hypotension; extensive surgical interventions; injuries; severe metabolic, endocrine, or water-electrolyte disorders; uncontrolled epilepsy; race (mongoloid race); simultaneous intake of fibrates.; For pills 40 mg; Renal failure of moderate severity (CC more than 60 ml / min); age over 70 years; history of liver disease; sepsis; hypotension; extensive surgical interventions; injuries; severe metabolic, endocrine, or water-electrolyte disorders; uncontrolled epilepsy.
Dosage and administration
The drug is taken orally. The tablet should be swallowed whole, washed down with water, not chewed or crushed. The drug can be taken at any time of the day, regardless of the meal.; Before treatment, the patient should begin to diet using low-cholesterol foods, which should be continued during the entire period of treatment.; The dose should be selected individually depending on the goals treatment and response to treatment, given the current generally accepted recommendations for target lipid concentrations. If necessary, use the drug at a dose of 5 mg is recommended to use rosuvastatin in another l carnal form or dosage, for example, 5 mg pills or 10 mg pills with a risk (a tablet at a dose of 10 mg should be divided into two parts according to the risk); the recommended initial dose of the drug is 5 mg or 10 mg 1 time / day as for patients previously not taking statins, and for patients transferred to the use of this drug after therapy with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.When choosing the initial dose, cholesterol levels should be taken into account in each individual patient and the possible risk of cardiovascular complications should be taken into account, as well as the potential risk of side effects should be evaluated. If necessary, the dose may be increased after 4 weeks. Due to the possible development of side effects with the use of the drug at a dose of 40 mg, compared with lower doses of the drug, titration to the maximum dose of 40 mg during 4 weeks of therapy can be carried out only in patients with severe hypercholesterolemia and with a high risk of cardiovascular complications (especially in patients with hereditary hypercholesterolemia), in whom the use of the drug in a dose of 20 mg did not achieve the desired effect of therapy and, and which will be under the supervision of a physician.; When prescribing the drug in a dose of 40 mg, careful monitoring of the patient is recommended. The prescription of the drug in a dose of 40 mg is not recommended for patients who have not previously consulted a doctor.; After 2-4 weeks of therapy and / or increasing the dose of the drug, monitoring of lipid metabolism indicators is necessary, if necessary, the dose should be adjusted.; The dose of the drug should be adjusted if necessary combined with drugs that increase the exposure of rosuvastatin. If exposure is expected to increase by 2 times or more, the initial dose of the drug should be 5 mg 1 time / day. The maximum daily dose of the drug should also be adjusted so that the expected exposure of rosuvastatin does not exceed that for a dose of 40 mg taken without simultaneous prescription of drugs interacting with rosuvastatin (see the section "Interaction with other drugs" Table 1) .; Elderly patients. dose adjustment is not required.; In patients with mild to moderate severity, dose adjustment is not required. In patients with severe renal failure (CC less than 30 ml / min), the use of the drug is contraindicated. Patients with moderate renal impairment are recommended an initial dose of 5 mg. The drug at a dose of 40 mg is contraindicated in patients with moderate renal dysfunction (CC 30-60 ml / min) .; The drug is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease. This fact should be taken into account when prescribing the drug to these groups of patients.When prescribing the drug in doses of 10 mg and 20 mg, the recommended initial dose of the drug for patients of the Mongoloid race is 5 mg. The use of the drug in a dose of 40 mg is contraindicated in such patients. When prescribing the drug in doses of 10 mg and 20 mg, the recommended initial dose for patients with a predisposition to myopathy is 5 mg. The use of the drug in a dose of 40 mg is contraindicated in such patients.