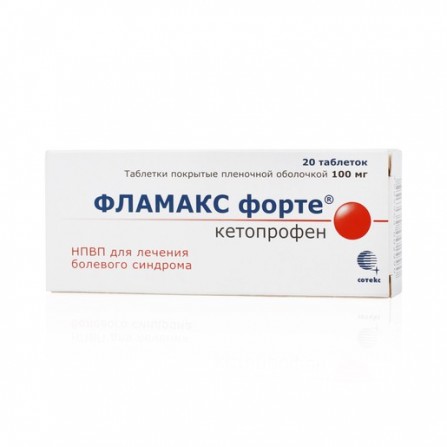
Flamax forte coated pills 100mg N20
Condition: New product
1000 Items
Rating:
Be the first to write a review!

More info
Description
Flamax forte is produced in the form of round biconvex blue coated pills. The drug has an analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, antiaggregatory effect and is used for the symptomatic treatment of pain and inflammation of various genesis of moderate intensity.
Release form
Pills
Composition
Ketoprofen, lactose monohydrate, rice starch, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, MCC, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, macrogol 6000, talc, titanium dioxide, brilliant blue.
Pharmacological effect
Flamax Forte has an analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, anti-aggregative effect. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs), a derivative of propionic acid. Suppresses the activity of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2, regulating the synthesis of prostaglandins. The analgesic effect is due to both central and peripheral mechanisms.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption - fast, bioavailability - 90%. Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen binds to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Cmax in plasma is reached quickly (within 0.5–2 hours after ingestion) due to low V d (0.1–0.2 l / kg). Css ketoprofen in plasma is achieved 24 hours after the start of its regular intake. Ketoprofen penetrates well into the synovial fluid and connective tissue. C max in synovial fluid is 30% of the serum concentration, and 4–6 hours after ingestion exceeds it. Ketoprofen penetrates the BBB. Almost completely metabolized in the liver by glucuronidation, has the effect of the first passage through the liver. Excreted by the kidneys (mainly) and by the intestines (1–8%). T 1/2 - 1.6–1.9 hours. In the elderly, T 1/2 increases to 3-5 hours, in patients with renal insufficiency (Cl creatinine 20-60 ml / min) is about 3.5 hours. Does not accumulate.
Indications
Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system: rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis), gouty arthritis (for an acute attack of gout, fast-acting dosage forms are preferable), osteoarthritis, pain syndrome: ophthalmic arthritis, ossalgia, ophthalmia bursitis, radiculitis, adnexitis, otitis media, headache and toothache, with cancer, post-traumatic and postoperative, accompanied by inflammation, algomenorrhea.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to ketoprofen or any component of the drug, a history of bronchial asthma caused by ketoprofen, another NSAID, incl. acetisalicylic acid, recurrent gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, peptic ulcer, severe hepatic impairment, severe renal failure, circulatory system failure, gastrointestinal, cerebrovascular and other bleeding (or suspected bleeding), pregnancy and breastfeeding, and pregnancy and breastfeeding period, pregnancy, and the period of breastfeeding, and pregnancy, and the period of breastfeeding, or pregnancy, and the period of nursing, breastfeeding, cerebrovascular and other bleeding up to 15 years), hemophilia and other blood coagulation disorders, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, diverticulitis.
Precautionary measures
Use with caution in anemia, bronchial asthma, alcoholism, tobacco smoking, alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, hyperbilirubinemia, liver and kidney (since the drug is mainly excreted by the kidneys) deficiency, diabetes mellitus, dehydration, sepsis, chronic heart failure, edema, arterial hypertension , Ischemic heart disease, blood diseases (including leukopenia), stomatitis, childhood (over 15 years old), old age.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation.
Dosage and administration
Inside, during the meal. Adults - on 1 tab. 2-3 times a day (every 8 hours). The maximum daily dose is 300 mg.
Side effects
On the part of the digestive system: NSAID-gastropathy, abdominal pain, dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting, heartburn, flatulence, loss of appetite, diarrhea), stomatitis, change in taste, ulceration and perforation of the gastrointestinal mucosa, gingival, gastrointestinal, hemorrhoidal bleeding increased serum hepatic transaminase activity, hepatitis. For the nervous system: headache, dizziness, insomnia, agitation, nervousness, drowsiness, depression, asthenia, confusion or loss of consciousness, forgetfulness, migraine, peripheral Naturopathic neuropathy. On the part of the senses: noise or tinnitus, blurred vision, conjunctivitis, dryness of the mucous membrane of the eye, pain in the eyes, conjunctival hyperemia, hearing loss, vertigo. On the part of the cardiovascular system: increased blood pressure, tachycardia. From the side of blood and blood-forming organs: rarely - agranulocytosis, anemia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia. On the part of the urinary system: edema syndrome, cystitis, urethritis, renal dysfunction, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, hematuria.On the part of the respiratory system: hemoptysis, dyspnea, bronchospasm, rhinitis, laryngeal edema, nosebleeds, shortness of breath. On the part of the skin: skin rash, alopecia and eczema, exudative erythema, incl. Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome), photodermatitis. Allergic reactions: skin rash (including erythematous, urticaria), itchy skin, rhinitis, angioedema, exfoliative dermatitis, anaphylactic shock. Other: increased sweating, myalgia, muscle twitching, thirst, vaginal bleeding.
Overdose
Symptoms: drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bleeding, liver and kidney dysfunction may occur. Treatment: symptomatic - gastric lavage and / or the use of activated carbon and / or other sorbents. There is no specific antidote.
Interaction with other drugs
Reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs, enhances the effect of anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, fibrinolytics, ethanol, side effects of GCS and mineralocorticosteroids, estrogens, reduces the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs and diuretics. Joint reception with other NSAIDs, GCS, ethanol, corticotropin can lead to the formation of ulcers and the development of gastrointestinal bleeding, an increase in the risk of developing renal dysfunction. The simultaneous appointment with oral anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytic agents, antiplatelet agents, cefoperazone, cefamundol and cefotetan increases the risk of bleeding. Increases the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs (dose recalculation is required). Inductors of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites. Joint appointment with sodium valproate causes a violation of platelet aggregation. Increases plasma concentration of verapamil and nifedipine, lithium preparations, methotrexate. Antacids and colestyramine reduce absorption. Myelotoxic drugs increase the hematotoxicity of the drug.
special instructions
With simultaneous use of ketoprofen and coumarin anticoagulants, incl.warfarin, or lithium salts, patients should be under the strict supervision of a physician. Care must be taken when prescribing the drug to patients with gastrointestinal ulcers in history, renal or hepatic insufficiency. During treatment, it is necessary to control the picture of peripheral blood and the functional state of the liver and kidneys. In case of impaired kidney and liver function (an increase in ALT activity is the most sensitive indicator of NSAID-induced liver dysfunction), a dose reduction and careful observation is necessary. If it is necessary to determine 17-keto steroids, the drug should be canceled 48 hours before the study. Like the rest of the drugs in this group, it can mask signs of an infectious disease. With the development of violations of the organs of sight is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist. During the period of treatment, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and psychomotor speed.