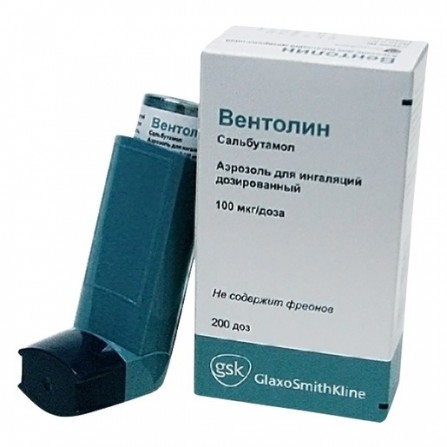
Ventolin aerosol for inhalation 200 doses
Condition: New product
986 Items
Rating:
Be the first to write a review!

More info
Active ingredients
Salbutamol
Release form
Spray
Composition
Salbutamol sulphate (micronized) 1dose-120.5 mcg **, 1 inhaler-28.92 mg Supplemental substances: propellant (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane) in 1 dose - up to 75 mg, in 1 inhaler - up to 18 g
Pharmacological effect
Selective β2-adrenoreceptor agonist. At therapeutic doses, it acts on β2-adrenergic receptors of the smooth muscles of the bronchi and has a short (4 to 6 h) bronchodilatory effect on β2-adrenergic receptors with a rapid onset of action (within 5 minutes) with reversible airway obstruction. It has a pronounced bronchodilatory effect, warning or arresting bronchospasm, decreases resistance in the airways. Increases VC. Increases mucociliary clearance (in chronic bronchitis up to 36%), stimulates the secretion of mucus, activates the function of the ciliated epithelium. At the recommended therapeutic doses, it does not adversely affect the cardiovascular system, does not cause an increase in blood pressure. To a lesser extent, compared with the drugs of this group, has a positive chrono - and inotropic effect. It causes expansion of the coronary arteries. It has a number of metabolic effects: reduces the concentration of potassium in the plasma, affects glycogenolysis and insulin secretion, has hyperglycemic (especially in patients with bronchial asthma) and lipolytic effect, increases the risk of acidosis.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption After an inhalation of 10-20% of the dose of salbutamol reach the lower respiratory tract. The rest of the dose remains in the inhaler or is deposited in the oropharynx and then swallowed. The fraction deposited in the respiratory tract is absorbed into the lung tissue and blood, but is not metabolized in the lungs. Distribution The binding of salbutamol to plasma proteins is 10%. . The swallowed part of the inhalation dose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes a significant metabolism during the first passage through the liver, turning into phenolic sulfate.Unchanged salbutamol and the conjugate are excreted mainly by the kidneys. Introduction The introduced salbutamol in / in T1 / 2 has 4-6 h. only a small fraction of the administered dose of salbutamol is excreted. Most of the dose of salbutamol administered intravenously, orally or by inhalation is excreted excreted for 72 hours.
Indications
Bronchial asthma: - relief of bronchial asthma symptoms when they occur; - prevention of bronchospasm attacks associated with allergen exposure or exercise; - use as one of the components during long-term maintenance therapy of bronchial asthma. Other chronic lung diseases accompanied by reversible airway obstruction , including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema. Bronchodilators should not be unified The main or main component of unstable or severe asthma therapy. In the absence of a reaction to salbutamol in patients with severe asthma, it is recommended to conduct GCS therapy in order to achieve and maintain control of the disease. A lack of response to salbutamol therapy may indicate the need for urgent medical advice or treatment.
Contraindications
- management of preterm labor; - threatened abortion; - hypersensitivity to the components of the drug or any other component of the preparation. Salbutamol should be used with caution in patients with thyrotoxicosis, tachyarrhythmia, myocarditis, heart defects, aortic stenosis, ischemic heart disease chronic heart failure, arterial hypertension, pheochromocytoma, decompensated diabetes mellitus, glaucoma.
Precautionary measures
In the course of treatment, exacerbation of psoriasis is possible. During pheochromocytoma, propranolol can be used only after taking an alpha blocker. After a long course of treatment, propranolol should be discontinued gradually,under the supervision of a doctor. Against the background of treatment with propranolol, it is necessary to avoid intravenous injection of verapamil, diltiazem. For several days before undergoing anesthesia, it is necessary to stop taking propranolol or to choose a remedy for anesthesia with minimal negative inotropic effect. The impact on the ability to drive vehicles and control mechanisms of patients whose activities require increased attention, the question of the use of propranolol on an outpatient basis should be addressed only after evaluating the individual response of the patient.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Fertility There is no data on the effects of salbutamol on human fertility. In preclinical studies, no adverse effect on the fertility of animals has been identified. Pregnancy During pregnancy, the drug should be prescribed only if the expected benefit of therapy for the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. jaws and malformations of the limbs, while taking salbutamol during pregnancy. In some of these cases, mothers took several concomitant medications during pregnancy. Due to the absence of a permanent nature of defects and a background frequency of congenital anomalies, ranging from 2 to 3%, a causal relationship with the use of the drug has not been established. when the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the baby. There is no evidence that salbutamol present in breast milk has a detrimental effect on the newborn.
Dosage and administration
The drug Ventolin is intended only for inhalation administration by inhalation through the mouth. An increased need for the use of beta2-adrenoreceptor agonists may be a sign of worsening bronchial asthma. In such a situation, it may be necessary to reassess the patient’s treatment regimen with consideration of the advisability of administering GCS concurrently. As an overdose may be accompanied by the development of adverse reactions,The dose or frequency of use of the drug can be increased only on the recommendation of a physician. The duration of action of salbutamol in most patients is from 4 to 6 hours. In patients who have difficulty synchronizing their breath using a metered-dose aerosol inhaler under pressure, a spacer can be used. In children and infants receiving the drug Ventolin, it is advisable to use a pediatric spacer device with a facial mask. For the relief of bronchospasm attacks for adults, the recommended dose makes 100 or 200 mkg; children - 100 micrograms, if necessary, the dose can be increased to 200 micrograms. It is not recommended to use the inhaler Ventolin often 4 times / day. The need for such frequent use of additional doses of the drug Ventolin or a sharp increase in the dose indicates a worsening course of asthma. To prevent attacks of bronchospasm associated with an allergen or exercise, adults - 200 mcg 10-15 minutes before the action of a provoking factor or load; children - 100 mcg for 10-15 minutes before exposure to a provoking factor or load, if necessary, the dose can be increased up to 200 mcg. With prolonged maintenance therapy for adults - up to 200 mcg 4 times / day; children - up to 200 mcg 4 times / day. Nebulizer Use Rules Inhaler Check Before using the inhaler for the first time, or if you did not use the inhaler for a week or longer, remove the cap from the mouthpiece, slightly squeezing the cap from the sides, shake the inhaler well and spray two air in order to ensure the health of the inhaler. Using the inhaler1. Remove the cap from the mouthpiece by slightly squeezing the cap from the sides. Inspect the mouthpiece inside and out to make sure it is clean. Shake the inhaler well. Keep the inhaler between the index finger and thumb in a vertical position, bottom up, with the thumb should be located on the base under the mouthpiece. Make a slow deep exhalation, clasp the mouthpiece with your lips without squeezing it with your teeth. Making the deepest possible inhale through the mouth simultaneously press the upper part of the inhaler to release one inhalation dose of salbutamol.Hold your breath for a few seconds, take the mouthpiece out of your mouth, then exhale slowly. To receive the second dose, keeping the inhaler in a vertical position, wait about 30 seconds and then repeat the steps. 3-7.9. Close the mouthpiece tightly with a protective cap. When performing stages 5, 6 and 7, you should not hurry. Inhale as slowly as possible, immediately before pressing the inhaler valve. The first few times it is recommended to practice in front of a mirror. If there is a fog coming out of the upper part of the inhaler or from the corners of the mouth, then you should start all over again from stage 2. If the doctor has given other instructions for using the inhaler, the patient should strictly follow them. If a patient has difficulty using an inhaler, then he needs to see a doctor. Inhaler cleaning The inhaler should be cleaned at least once a week. Remove the metal can from the plastic case and remove the mouthpiece cap.2. Thoroughly rinse the plastic casing and the mouthpiece cap under a stream of warm water. Dry the plastic case and the mouthpiece cover completely both outside and inside. Do not overheat. Place the metal can into the plastic case and put the mouthpiece cover on. Do not immerse the metal can in water.
Side effects
The adverse reactions listed below are listed according to the damage to organs and organ systems and the frequency of occurrence. The frequency of occurrence is determined as follows: very often (> 1/10), often (> 1/100 and <1/10), infrequently (> 1/1 000 and <1/100), rarely (> 1/10 000 and <1/1 000), very rarely (<1/10 000, including individual cases). The frequency categories were formed based on clinical studies of the drug and post-registration observation. From the immune system: very rarely - hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema, urticaria, bronchospasm, decrease in blood pressure and collapse. From the side of metabolism and nutrition: rarely - hypokalemia. Beta2-agonist therapy can lead to clinically significant hypokalemia. On the nervous system: often - tremor, headache; very rarely - hyperactivity. On the side of the heart: often - tachycardia; infrequently - a feeling of heartbeat; very rarely - arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation,supraventricular tachycardia and extrasystoles). From the side of the vessels: rarely - peripheral vasodilation. From the side of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinum: very rarely - paradoxical bronchospasm. From the side of the gastrointestinal tract: muscle and connective tissue: infrequently - muscle cramps.
Overdose
Symptoms: signs and symptoms of an overdose of salbutamol are transient phenomena pharmacologically mediated by stimulation of beta-adrenoreceptors (see sections Special Instructions and Side Effects), such as a decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia, muscle tremor, nausea, vomiting. The use of large doses of salbutamol can cause metabolic changes, including hypokalemia, it is necessary to control the concentration of potassium in the blood serum. Treatment: when used in high doses, as well as overdose of short-acting beta-agonists, the development of lactate acidosis was observed, therefore, overdose can be shown control over the increase in serum lactate and the possibility of the development of metabolic acidosis (especially with the preservation or worsening of tachypnea, despite the elimination of other signs of Bronchorus Azman such as wheezing).
Interaction with other drugs
It is not recommended to use salbutamol and non-selective β-adrenoreceptor blockers such as propranolol at the same time. Salbutamol is not contraindicated in patients who receive monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO). In patients with thyrotoxicosis, Ventolin stimulates the action of CNS stimulants, tachycardiophenone, and I am using the IOPA, and I am using the IOP, I, I, I, I, I, and I will apply for the IOP, stimulating the CNS, and I’ll use the shit, I will need to put out patterns for teofillin, I will apply and I will now need to use the shit, and I will need to go to the table and I am using the IoTell, I will apply for the hemodynamic insulin receptor. increase the likelihood of developing tachyarrhythmias. Simultaneous administration with anticholinergics (including inhalants) may contribute to an increase in intra eye pressure. Diuretics and corticosteroids enhance the hypokalemic effect of salbutamol.
special instructions
Bronchial asthma treatment is recommended in stages, controlling the patient's clinical response to treatment and lung function. Bronchodilators should not be the only or main component of unstable or severe asthma therapy. Increasing the need for short-acting bronchodilators, in particular beta2-adrenoreceptor agonists, to alleviate symptoms of bronchial asthma indicates a worsening course of the disease. In such cases, the patient’s treatment plan should be reviewed.A sudden and progressive worsening of bronchial asthma can pose a potential threat to the patient's life, therefore in such situations, the advisability of prescribing or increasing the dose of GCS should be considered. In patients at risk, daily peak expiratory flow rate monitoring is recommended. The therapy with beta2-adrenoreceptor agonists, especially when administered parenterally or using a nebulizer, can lead to hypokalemia. intensified as a result of the simultaneous use of xanthine derivatives, GCS, diuretics, and also due to hypoxia. In such situations, it is recommended to control the concentration of potassium in the blood serum. As with the use of other agents for inhalation therapy, when taking salbutamol, paradoxical bronchospasm may develop with increased wheezing immediately after the use of the drug. This condition requires immediate treatment using an alternative form of salbutamol or another short-acting inhaled bronchodilator. The drug Ventolin should be immediately canceled, evaluate the patient's condition and, if necessary, prescribe another fast-acting bronchodilator to continue treatment. - or additional measures. Patients should be instructed on the proper use of the Ventolin inhaler. The effect on the ability to drive vehicles and There is no data available for the mechanisms.