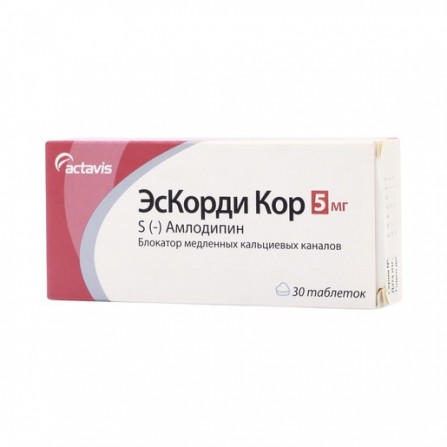
Eskordi core pills coated 5mg N30
Condition: New product
1000 Items
Rating:
Be the first to write a review!

More info
Active ingredients
Levamlodipine
Release form
Pills
Composition
1 tablet contains: Active substance: S (-) amlodipine (in the form of besylate) 5 mg. Auxiliary substances: microcrystalline cellulose - 46.367 mg, lactose - 40.767 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide - 1.4 mg, magnesium stearate - 4.2 mg, croscarmellose sodium - 4.2 mg, iron oxide yellow - 0.8 mg.
Pharmacological effect
Slow calcium channel blocker, a dihydropyridine derivative. S (-) isomer has a more pronounced pharmacological action than R (+) amlodipine. It has antianginal and hypotensive effects. By binding to the dihydropyridine receptors S (-), amlodipine is more potent than the R (+) isomer, blocks calcium channels, reduces the transmembrane transition of calcium ions into the cell (to a greater extent in vascular smooth muscle cells than in cardiomyocytes). There is a long dose-dependent hypotensive Effect. The hypotensive effect is due to the direct vasodilating effect on vascular smooth muscle. In hypertension, a single dose provides a clinically significant reduction in blood pressure for 24 hours (in the position of the patient lying and standing). The onset of the effect is 2-4 hours, the duration of the effect is 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and distribution After ingestion (single dose 2.5 mg) S (-) amlodipine is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The average absolute bioavailability is 65%. Cmax in serum (8.30 ± 1.071 ng / ml) is observed after 2.73 ± 0.88 h. Css is reached after 7 days of therapy. Eating does not affect the absorption of S (-) amlodipine. Plasma protein binding - 93%. The average Vd is 21 l / kg body weight, which indicates that most of the drug is in the tissues, relatively less in the blood. The drug penetrates through the BBB. Metabolism S (-) amlodipine undergoes a slow but extensive metabolism (90%) in the liver with the formation of inactive metabolites. Exposed to first pass through the liver. Metabolites do not have significant pharmacological activity. Output After a single dose, T1 / 2 varies from 14.62 to 68.88 hours. When reappointed, T1 / 2 is approximately 45 hours. About 60% of the ingested dose is excreted by the kidneys mainly in the form of metabolites; 10% - in unchanged form, and 20-25% through the intestines, as well as with breast milk.The total clearance of S (-) amlodipine is 0.116 ml / s / kg (7 ml / min / kg, 0.42 l / h / kg). Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations In elderly patients (over 65), the elimination of S (-) amlodipine is slow (T1 / 2 - about 65 hours) compared with young patients, but this difference has no clinical significance. The T1 / 2 extension in patients with hepatic insufficiency suggests that with prolonged use, the cumulation of the drug in the body will be higher (T1 / 2 - up to 60 hours). Renal failure has no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of S (-) amlodipine. When hemodialysis S (-) amlodipine is not removed.
Indications
Arterial hypertension I (mild) severity (in combination with other antihypertensive drugs or as monotherapy).
Contraindications
- Prinzmetal's angina pectoris; - severe arterial hypotension; - collapse; - cardiogenic shock; - pregnancy; - lactation (breastfeeding) period; - children and adolescents under 18 years of age (efficacy and safety not established); - hypersensitivity to S (- a) amlodipine and other dihydropyridine derivatives.
Precautionary measures
During the period of treatment with Escordi Cor, control over body weight and sodium intake, the appointment of an appropriate diet is necessary. It is necessary to maintain dental hygiene and frequent visits to the dentist (prevention of pain, bleeding and gum overgrowth.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Use of the drug is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
Dosage and administration
The drug is taken orally 1 time per day. The recommended starting dose of Escordi Cor is 2.5 mg. With insufficient therapeutic effect, the dose can be increased to 5 mg.
Side effects
From the side of cardiovascular system: feeling of heartbeat, shortness of breath, excessive decrease in blood pressure, fainting, vasculitis, edema (swelling of ankles and feet), flushing of blood to the face; rarely - rhythm disturbance (bradycardia, ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation), chest pain, orthostatic hypotension; very rarely - development or aggravation of heart failure, migraine. For the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: dizziness, headache, fatigue, drowsiness, mood changes; rarely - convulsions, loss of consciousness, hyperesthesia,nervousness, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo, asthenia, indisposition, insomnia, depression, unusual dreams; very rarely - ataxia, apathy, agitation, amnesia. On the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain; rarely, increased liver enzymes, jaundice (due to cholestasis), pancreatitis, dry mouth, flatulence, gum hyperplasia, constipation, diarrhea; very rarely - gastritis, increased appetite, impaired taste. From the genitourinary system: rarely - pollakiuria, painful urge to urinate, nocturia, reduced potency; very rarely - dysuria, polyuria. Dermatological reactions: very rarely - xerodermia, alopecia, dermatitis, purpura, discoloration of the skin. Allergic reactions: pruritus, rash (including erythematous, maculo-papular rash, urticaria), angioneurotic edema . On the part of the musculoskeletal system: rarely - arthralgia, arthrosis, myalgia (with prolonged use); very rarely - myasthenia. From the senses: rarely - visual disturbances, conjunctivitis, diplopia, pain in the eyes, tinnitus; very rarely - parosmia, disturbance of accommodation, xerophthalmia. On the part of the respiratory system: rarely - dyspnea, nasal bleeding; very rarely - cough, rhinitis. Others: rarely - gynecomastia, polyurikemia, increase / decrease in body weight, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hyperglycemia, increased sweating, thirst, back pain; very rarely - cold sticky sweat.
Overdose
Symptoms: excessive decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia, excessive peripheral vasodilation. Treatment: gastric lavage, the appointment of activated carbon, maintaining the function of the cardiovascular system, monitoring the performance of the heart and lungs, elevated position of the lower extremities, control of BCC and diuresis. To restore vascular tone - the use of vasoconstrictor agents (in the absence of contraindications to their use). To eliminate the effects of calcium channel blockade - in / in the introduction of calcium gluconate. Hemodialysis is not effective.
Interaction with other drugs
Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation increase the concentration of amlodipine in the blood plasma, increasing the risk of side effects, and inductors of microsomal liver enzymes decrease. The antihypertensive effect is weakened by alpha-adrenostimulyatory,estrogens (sodium retention), sympathomimetics. Thiazide and loop diuretics, beta-blockers, verapamil, ACE inhibitors and nitrates enhance the antianginal and hypotensive effects. Amiodarone, quinidine, alpha1-blockers, antipsychotics (neuroleptics), quinidine, alpha1-adrenergic blockers, antipsychotics (neuroleptics), and adolestools and adolesophobia, adolesopholes and adolescents; action. Does not affect the pharmacokinetic parameters of digoxin and warfarin. Cimetidine does not affect the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine. When used together with lithium preparations, it is possible neurotoxicity (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, ataxia, tremor, tinnitus). Calcium preparations can reduce the effect of slow calcium channel blockers. Procainamide, quinidine and other drugs that prolong the QT interval, increase the negative inotropic effect and can increase the risk of a significant lengthening of the QT interval. Grapefruit juice may reduce the concentration of amlodipine in the blood plasma, but this decrease is so small that it does not significantly change the effect of amlodipine.
special instructions
In elderly patients, the T1 / 2 and clearance of the drug may be lengthened. Dosing regimen for the elderly is the same as for patients of other age groups. With increasing doses, careful monitoring of elderly patients is necessary. Despite the fact that the calcium channel blockers do not have withdrawal syndrome, a gradual reduction in dose is recommended before stopping treatment. Impact on the ability to drive and control mechanisms Some patients, mainly at the beginning of treatment, may experience drowsiness and dizziness. When they occur, special precautions should be taken when driving and working with machinery.