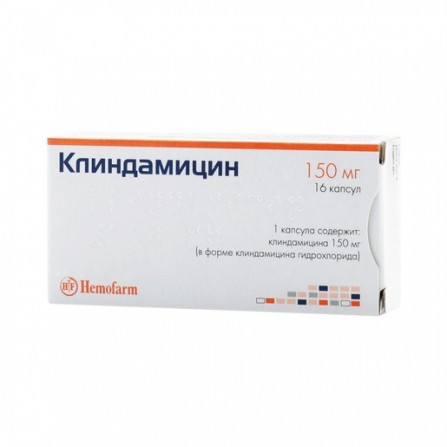
Clindamycin capsules 150mg N16
Condition: New product
991 Items
Rating:
Be the first to write a review!

More info
Active ingredients
Clindamycin
Release form
Capsules
Composition
1 capsule contains: Active substance: clindamycin (in the form of hydrochloride) 150 mg. Adjuvants: corn starch, lactose monohydrate, talc, magnesium stearate. Composition of the capsule body: azorubine dye (E122), brilliant black dye (E151), gelatin. Composition capsule caps: titanium dioxide (E171), quinoline yellow dye (E104), azorubine dye (E122), crimson dye Ponzo 4R (E124), diamond black dye (E151), gelatin.
Pharmacological effect
Clindamycin is a drug from the group of antibiotics - lincosamides, has a broad spectrum of action, is bacteriostatic, binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome and inhibits protein synthesis in microorganisms. Active against Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus epidermidis producing penicillinase), Streptococcus spp. (excluding Enterococcus spp.), Streptococcus pneumoniae, anaerobic and microaerophilic gram-positive cocci (including Peptococcus spp. and Peptostreptococcus spp.), Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium tetani, Myrophromyphromaphromaphrophymus, diphtheriae, Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium tetani, Myrophromaphroma, anesthesomephromaphroma, anesthesia, anesthesia, ancephroma, anesthesia, anesthesia, anesthesia, anesthesia, anesthesia, anesthesia, anesthetic, anesthesia, anesthesia, anesthesia, anesthetic, anesthetic (including Bacteroides fragilis and Bacteroides melaningenicus), anaerobic textures that do not form spores, bacilli (including Propionibacterium spp., Eubacterium spp., Actinomyces spp.). Most of the strains of Clostridium perfringens are sensitive to Clindamine, you can not apply them if you have other types of artistes that are clindamic, they do not develop spores. ) are resistant to the action of the drug, therefore for infections caused by Clostridium spp., the definition of an antibiogram is recommended. According to the mechanism of action and the antimicrobial spectrum, it is close to lincomycin (for some types of microorganisms, especially for bacteroids and their anaerobes, 2-10 times more potent).
Pharmacokinetics
Quickly and completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, simultaneous ingestion of food slows down absorption without changing the drug concentration in plasma. Easily penetrates biological fluids and tissues (tonsils, muscle and bone tissue, bronchi, lungs, pleura, bile ducts, appendix, fallopian tubes, prostate gland, synovial fluid, saliva, sputum, wound surfaces); passes through the BBB poorly (with inflammation of the meninges, the permeability of the BBB increases). Cmax in the blood is achieved by oral administration after 0.75-1 h, after i / m administration - after 1 h in children and 3 h in adults, with iv administration - by the end of the infusion. At therapeutic concentration it circulates in the blood for 8- 12 h, T1 / 2 is about 2.4 h; it is metabolized mainly in the liver (70-80%) with the formation of active (N-dimethylcindamycin and clindamycin sulfoxide) and inactive metabolites; excreted within 4 days by the kidneys (10%) and through the intestines (3.6%) as an active drug, the rest as inactive metabolites.
Indications
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to clindamycin; - Infections of the upper respiratory tract and infections of upper respiratory tract (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis), lower respiratory tract (pneumonia, including aspiration, lung abscess, pleural empyema , bronchitis), scarlet fever, diphtheria; - Infections of the urogenital tract (chlamydia, endometritis, vaginal infections, tubo-ovarian inflammation); - Infections of the skin and soft tissues (infected wounds, abscesses, boils, felons), abdominal cavity (peritonitis, abs Cess), oral cavity; - Acute and chronic osteomyelitis; - Septicemia (primarily anaerobic); - Bacterial endocarditis; - Prevention of peritonitis and intra-abdominal abscesses after perforation of the intestine or as a result of traumatic infection (in combination with aminoglycosides).
Contraindications
- Myasthenia; - Bronchial asthma; - Ulcerative colitis (in history); - Rare hereditary diseases such as: galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption (for capsules); - Pregnancy; - Lactation; - Children up to 3 -years - for a solution for iv administration and intramuscular injection (due to the lack of data on the safety of using benzyl alcohol); - Children's age up to 8 years for capsules (average child weight less than 25 kg); - Increased sensitivity Clindamycin is used with caution in patients with severe hepatic and / or and renal failure in elderly patients.
Precautionary measures
With the development of hypersensitivity reactions, treatment with clindamycin should be discontinued and (if necessary) appropriate therapy should be given. Anti-bacterial drugs suppress the normal intestinal flora, which may contribute to increased reproduction of clostridia. Cases of pseudomembranous colitis of varying severity, even life-threatening, have been observed with virtually all antibacterial agents, including clindamycin. Toxins produced by Clostridium difficile have been shown to be the main cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. Diarrhea, colitis, symptoms of pseudomembranous colitis can appear both in patients receiving clindamycin and 2-3 weeks after stopping treatment.Pseudomembranous colitis is manifested by diarrhea, leukocytosis, fever, and abdominal pain (sometimes accompanied by discharge of blood and mucus from the stool). Therefore, in all cases of diarrhea after taking antibacterial drugs should consider the possibility of this diagnosis. After making a diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis in mild cases, it is enough to cancel treatment and use ion exchange resins (Kolestiramine, Colestipol), in cases of moderate severity and in severe cases, the loss of fluid, electrolytes and protein is indicated, the prescription of an antibacterial drug effective against Clostridium difficile (for example vancomycin or metronidazole). It should be remembered that the use of local dosage forms may exhibit systemic effects. With external use of clindamycin, pseudomembranous colitis has rarely developed, but with intravaginal use it has not been observed. In patients over 60 years old, antibiotic-associated colitis and diarrhea (caused by Clostridium difficile) are more common and may be more severe (you should carefully monitor patients and the frequency stool so that diarrhea does not develop). When clindamycin is used, excessive growth of microorganisms that are insensitive to it, especially yeast-like fungi, is possible. With the development of superinfection, appropriate measures should be taken depending on the clinical situation. When administered in high doses, control of plasma clindamycin concentration is necessary. If the treatment is carried out over an extended period of time, then liver and kidney function tests should be carried out regularly.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Contraindicated.
Dosage and administration
Inside, adults and children over 15 years old (average weight of a child 50 kg and above) for moderately ill diseases, 1 capsule (150 mg) is prescribed 4 times / day (every 6 hours). In severe infections to adults and children over 15, a single dose It can be increased to 2-3 capsules (300-450 mg). With the / m and / in the introduction of the recommended dose for adults - 300 mg 2 times / day. For severe infections - up to 1.2-2.7 g / day, divided into 3-4 introductions. It is not recommended in / m the appointment of a single dose exceeding 600 mg. The maximum single dose for iv administration is 1.2 g for 1 hour. Children over 3 years old are 15-25 mg / kg / day, divided into 3-4 equal doses.In severe infections, the daily dose can be increased to 25–40 mg / kg body weight, divided into 3–4 identical injections. Patients with severe hepatic and / or renal insufficiency do not need to adjust the dosage regimen in case of administration of the drug at least 8 hours apart. For on / in the introduction of the drug is diluted to a concentration of not higher than 6 mg / ml; diluted solution is injected into / in drip for 10-60 minutes. It is not recommended to administer the drug in / in the jet. Dilution and duration of infusion are recommended to be done according to the dose - volume of solvent - duration of infusion (respectively): 300 mg - 50 ml - 10 min ; 600 mg - 100 ml - 20 min; 900 mg - 150 ml - 30 min; 1200 mg - 200 ml - 45 min. The following solutions can be used as a solvent: 0.9% sodium chloride solution and 5% dextrose solution.
Side effects
On the part of the digestive system: dyspepsia (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), esophagitis, jaundice, liver dysfunction, hyperbilirubinemia, dysbacteriosis, pseudomembranous enterocolitis. hematopoietic organs: leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia. Allergic reactions: rarely - maculopapular rash, urticaria, pruritus; in some cases, exfoliative and vesicular-dermatitis, eosinophilia, anaphylactoid reactions. From the side of the cardiovascular system: with rapid IV injection, a decrease in blood pressure, up to collapse; dizziness, weakness. Local reactions: irritation, soreness (in the place of intramuscular injection), thrombophlebitis (in the place of intravenous injection). Others: development of superinfection.
Overdose
In case of overdose, side effects may increase. Treatment: symptomatic therapy, there is no specific antidote. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are ineffective.
Interaction with other drugs
Clindamycin enhances (mutually) the effect of rifampicin, streptomycin aminoglycosides, gentamicin (especially in the treatment of osteomyelitis and the prevention of peritonitis after intestinal perforation). and magnesium sulfate. Shows antagonism with erythromycin and chloramphenicol. It is not recommended to use simultaneously with solutions containing a complex of vitamins groups B, aminoglycosides,phenytoin. Simultaneous administration with antidiarrheal drugs increases the risk of developing pseudomembranous colitis. When used simultaneously with opioid (narcotic) analgesics, they can increase their respiratory depression (even apnea).
special instructions
Pseudomembranous colitis can appear both on the background of clindamycin intake, and 2-3 weeks after stopping treatment (3-15% of cases); manifested by diarrhea, leukocytosis, fever, abdominal pain (sometimes accompanied by the release of blood and mucus from the stool). In these cases, in mild cases, it is enough to cancel treatment and use ion-exchange resins (Kolestiramine, Colestipol), in severe cases compensation of fluid loss is indicated, electrolytes and protein, the appointment of vancomycin inside or metronidazole. Do not use drugs that inhibit intestinal motility. The safety of the drug in children under 3 years old has not been established. With long-term therapy, children need periodic monitoring of blood formulas and the functional state of the liver. When prescribing the drug in high doses, control of plasma clindamycin concentration is necessary. Patients with severe liver failure need to monitor liver function (liver enzymes).