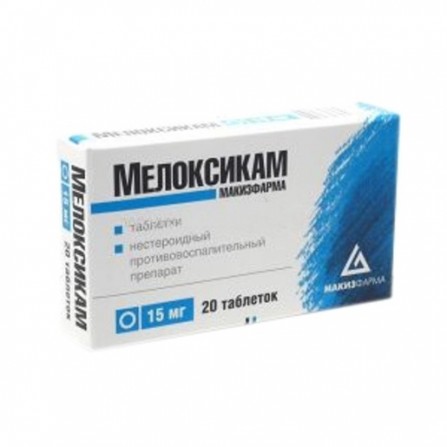
Meloxicam Stad pills 15mg N20
Condition: New product
1000 Items
Rating:
Be the first to write a review!

More info
Active ingredients
Meloxicam
Release form
Pills
Composition
Meloxicam 15 mg; Auxiliary substances: microcrystalline cellulose, lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide (aerosil), croscarmellose sodium, talc, magnesium stearate.
Pharmacological effect
NSAIDs. It has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effect. The mechanism of action is due to inhibition of the enzymatic activity of COX-2, which is involved in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins in the area of inflammation. To a lesser extent, meloxicam acts on COX-1, which is involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins, which protect the gastrointestinal mucosa and are involved in the regulation of blood flow in the kidneys.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption; Well absorbed from the digestive tract. The absolute bioavailability of meloxicam is 89%. Simultaneous food intake does not affect absorption. The concentration of meloxicam when taking the drug orally in doses of 7.5 and 15 mg is proportional to the dose.; Distribution; The equilibrium state is reached within 3-5 days of regular intake. With prolonged (more than 1 year) use of the drug, the concentration of meloxicam is similar to Css, which was established after the first days of taking the drug. Plasma protein binding is more than 99%. When taking the drug 1 time / day, Cssmin and Cssmax differ to a small extent and are at a dose of 7.5 mg 1 time / day 0.4-1.0 mcg / ml, and when taken at a dose of 15 mg 1 time / day - 0.8-2.0 mcg / ml, respectively. Meloxicam penetrates histohematogenous barriers, the concentration in synovial fluid reaches 50% Cmax in plasma. Vd averages 11 l.; Metabolism; Meloxicam is almost completely metabolized in the liver to form four pharmacologically inactive metabolites. The main one is 5'-carboxymeloxicam (60% of the dose), which is formed by oxidation of the intermediate metabolite - 5'-hydroxymethylmeloxicam (9% of the dose). In vitro studies have established that biotransformation occurs with the participation of CYP2C9, CYP3A4 isoenzyme is of additional importance. Peroxidase is involved in the formation of two other metabolites (constituting 16% and 4% of the dose, respectively), the activity of which is likely to vary individually.With feces in unchanged form, less than 5% of the daily dose is excreted, in the urine, unchanged form of the drug is found only in trace amounts. T1 / 2 - 15-20 hours. Plasma clearance averages 8 ml / min; Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations; In elderly people, the clearance of the drug decreases. In patients with moderate or moderate hepatic or renal failure, meloxicam pharmacokinetics does not change significantly .
Indications
Symptomatic treatment: - osteoarthritis; - rheumatoid arthritis; - ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis).
Contraindications
- "Aspirin" bronchial asthma; - peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase; - bleeding of various genesis (including from the gastrointestinal tract, cerebrovascular); - severe renal failure (if hemodialysis is not performed); - severe liver failure; - severe heart failure; - children's age up to 15 years; - pregnancy; - lactation (breastfeeding); - hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. With caution should use the drug in the elderly and in patients with erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract in history.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
The drug is contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding) .; The use of Meloxicam, like other drugs that block the synthesis of prostaglandins, can affect fertility, so it is not recommended for women who want to become pregnant.
Dosage and administration
In rheumatoid arthritis, the recommended dose is 15 mg / day; depending on the therapeutic effect, the dose can be reduced to 7.5 mg / day; With osteoarthritis, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 7.5 mg / day, in the absence of effect the dose can be increased to 15 mg / day; With ankylosing spondyloarthritis the daily dose is 15 mg The maximum daily dose should not exceed 15 mg. The drug is taken 1 time / day during the meal. In patients with an increased risk of side effects, as well as in patients with severe impaired renal function on hemodialysis, the dose should not exceed 7.5 mg / day; Patients with impaired renal function (CC more than 25 ml / min) do not need to adjust the dosage regimen.
Side effects
On the part of the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, perforation of the stomach or intestines, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (hidden or obvious), increased activity of liver enzymes, hepatitis, colitis, stomatitis, dry mouth, esophagitis.; On the part of the cardiovascular system: tachycardia, increased blood pressure, tidal sensation; On the part of the respiratory system: exacerbation of bronchial asthma.; On the part of the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, tinnitus, disorientation, confusion thoughts on loss of sleep.; From the urinary system: edema, interstitial nephritis, renal medullary necrosis, urinary tract infection, proteinuria, hematuria, renal failure.; Dermatological reactions: itching, skin rash, urticaria, increased photosensitivity.; From the hemopoietic system: anemia , leukopenia, thrombocytopenia; Allergic reactions: anaphylactoid reactions (including anaphylactic shock), swelling of the lips and tongue, allergic vasculitis, erythema multiforme exudative (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome); Other: fever.
Overdose
Symptoms: impaired consciousness, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, acute renal failure, liver failure, respiratory arrest, asystole. Treatment: gastric lavage, taking activated charcoal (within 1 h after taking the drug); if necessary, conduct symptomatic therapy. Kolestiramin accelerates the elimination of meloxicam from the body. Forced diuresis, alkalization of urine, hemodialysis are ineffective due to the high degree of binding of meloxicam with blood proteins. There is no specific antidote.
Interaction with other drugs
With simultaneous use with other NSAIDs (including acetylsalicylic acid), the risk of erosive and ulcerative lesions and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract increases. With simultaneous use with antihypertensive drugs, a decrease in the effectiveness of the latter is possible. With simultaneous use with lithium preparations, development is possible cumulation of lithium and an increase in its toxic action (it is recommended to control the concentration of lithium in the blood); whileuse with methotrexate increases the likelihood of anemia and leukopenia (periodic blood count is shown) .; If used concurrently with diuretics and cyclosporine, the risk of developing renal failure increases. If used simultaneously with intrauterine contraceptives, they may decrease use with anticoagulants (including with heparin, ticlopidine, warfarin), as well as with thrombolytic drugs (including with streptoks nasal, fibrinolysin) increases the risk of bleeding (requires periodic monitoring of blood clotting); With simultaneous use of Kolestiramin, meloxicam excretion through the gastrointestinal tract (due to binding).
special instructions
Care should be taken when using the drug in patients with indications of a history of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer and in patients receiving anticoagulants, as such patients have an increased risk of erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.; Care should be taken to monitor renal function when using the drug in elderly patients, patients with chronic heart failure, patients with cirrhosis of the liver, as well as in patients with hypovolemia as a result interventions.; Patients taking diuretics and meloxicam at the same time should receive a sufficient amount of liquid. When allergic reactions occur (itching, skin rash, urticaria, photo sensitization) should stop taking the drug.; Meloxicam, as well as other NSAIDs, can mask the symptoms of infectious diseases.; Influence on ability to drive vehicles and control mechanisms; Against the background of the drug use, the patient should not engage in potentially hazardous activities that require increased attention, because may cause headache, dizziness, drowsiness.